IoT and Emerging Technologies: Practical Advances in AR/VR, Agritech, and CleanTech

- Introduction
- IoT: The Foundation of Emerging Technologies
- AR/VR Hardware: Technical Progress and Real-World Use
- Agritech: Precision, Automation, and Data-Driven Farming
- CleanTech: Renewable Energy, Smart Grids, and Environmental Monitoring
- Technical Challenges and Solutions in IoT
- Actionable Insights and Recommendations
- Final Thoughts on IoT & Emerging Technologies
- About DesignToDevice
- Why trust DesignToDevice?
- Want to learn more?
- Sign Up To Our Newsletter
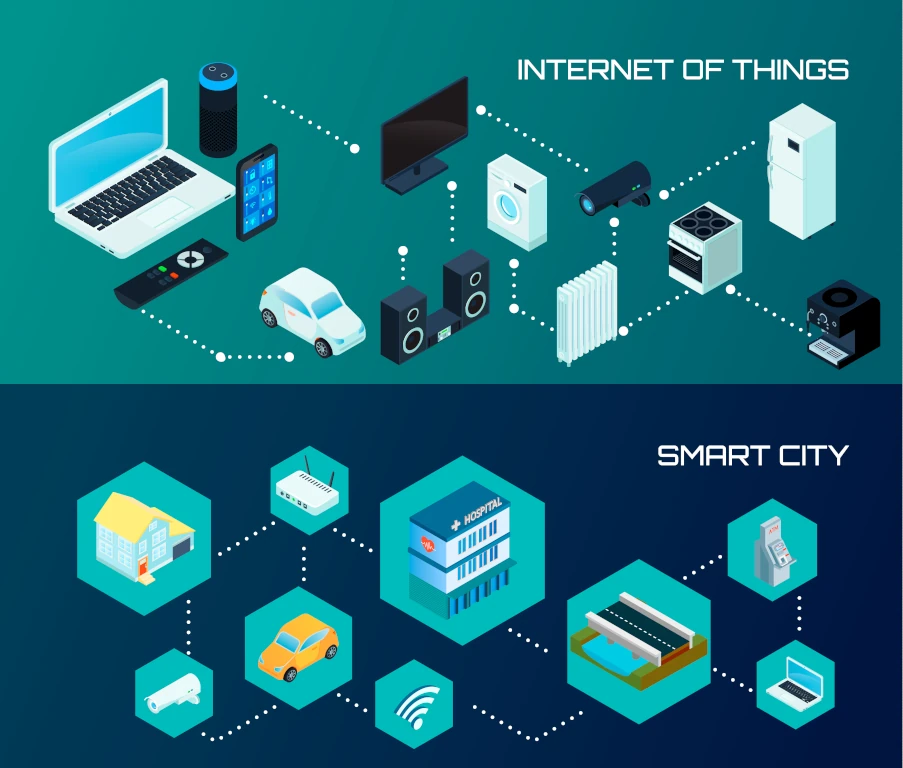
Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) is changing how we interact with the physical and digital worlds. By embedding connectivity and intelligence into everyday objects, IoT enables a level of automation, insight, and responsiveness that was previously impossible. From wearable devices to smart factories, the integration of IoT into products and systems is creating more dynamic, efficient, and user-centric experiences.
What makes IoT especially powerful is its role as a foundational layer for emerging technologies. When combined with fields like augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), agriculture technology (Agritech), and clean energy (CleanTech), IoT serves as the nervous system—gathering real-time data, triggering automated responses, and supporting intelligent decision-making. These integrations aren’t futuristic—they’re already driving measurable outcomes in productivity, sustainability, and user engagement.
This blog explores the technical advancements and practical applications of IoT across these key sectors. Whether you’re designing smart hardware, deploying automation solutions, or looking to stay ahead in digital transformation, understanding how IoT connects the dots is essential. You’ll gain insight into real-world use cases, the latest device-level innovations, and strategic recommendations for leveraging IoT in fast-moving industries.
IoT: The Foundation of Emerging Technologies
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the backbone of digital transformation across industries. By connecting physical devices, ranging from simple sensors to complex machinery, to digital systems, IoT enables real-time data collection, analysis, and control. This connectivity is essential for the development and deployment of advanced applications in AR/VR, Agritech, and CleanTech. The ability to gather and process data from diverse sources allows organizations to make informed decisions, automate processes, and respond quickly to changing conditions.
Core Technologies Enabling IoT
Modern IoT architecture is built on several key technical features. Sensors and actuators are the foundation, collecting data on variables such as temperature, motion, humidity, and pressure. These devices are now more energy-efficient and capable of continuous monitoring, thanks to advances in low-power chip design. Connectivity is achieved through a range of protocols, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, cellular networks (4G/5G), and LPWAN technologies like LoRaWAN and NB-IoT. The choice of protocol depends on the application’s requirements for range, bandwidth, and power consumption.
Edge computing has become a standard practice, allowing data to be processed close to the source for faster response times and reduced bandwidth usage. This is especially important for time-sensitive applications in manufacturing and agriculture. Cloud integration provides scalable storage and advanced analytics, enabling organizations to analyze large datasets for long-term insights and predictive modeling.
Architecting Secure and Scalable IoT Systems
Implementation of IoT systems requires careful planning and adherence to industry standards. The latest IoT architectures are modular and layered, often including dedicated layers for data management, analytics, and security. Protocols such as MQTT, CoAP, and Matter ensure reliable and interoperable communication between devices. Security is embedded at every layer, with zero-trust models, hardware-based security modules, and continuous monitoring to address evolving threats.
Organizations are encouraged to follow frameworks like the IoT Security Maturity Model (SMM) and the Cloud Security Alliance’s IoT Security Controls Framework to assess and improve their security posture. As IoT networks scale, edge-cloud synergy and system disaggregation support efficient data flow and future-proofing.
Key points of The Foundation of Emerging Technologies

AR/VR Hardware: Technical Progress and Real-World Use
Hardware Developments
AR/VR hardware has seen rapid advancements in display technology, processing power, and ergonomics. Devices like the Meta Quest 3, Pico 5, Apple Vision Pro, and Meta Orion AR are now lighter, wireless, and equipped with high-resolution displays. For example, the Apple Vision Pro features an OLED micro display with a resolution of 3660 x 3200 per eye, eye tracking, and spatial audio, making it suitable for both consumer and enterprise use. The Meta Quest 3 and Pico 5 offer LCD displays with resolutions above 2000 x 2000 per eye, standalone operation, and advanced hand tracking. These improvements have made AR/VR headsets more comfortable for extended use and accessible to a wider audience.
| Device | Display Type | Resolution (per eye) | Connectivity | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meta Quest 3 | LCD | 2064 x 2208 | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth | Standalone, hand tracking |
| Pico 5 (rumored to be canceled) | LCD | 2160 x 2160 | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth | Lightweight, wireless |
| Apple Vision Pro | OLED Microdisplay | 3660 x 3200 | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth | Eye tracking, spatial audio |
| Meta Orion AR | LCD | 70° FOV (Field of View) | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth | Everyday AR, wide field of view |
The technical progress in AR/VR hardware is driven by advanced chipsets like the Snapdragon XR2 Gen 2, which enable higher graphical performance and mixed reality features. Innovations such as foveated rendering and depth-sensing cameras enhance realism and interactivity. The trend toward standalone, untethered operation is clear, with most new headsets offering wireless connectivity and onboard processing, reducing the need for external computers or cables. These features are especially valuable in enterprise settings, where mobility and ease of deployment are critical.
Enterprise adoption of AR/VR is accelerating, particularly in manufacturing, healthcare, and retail. In manufacturing, AR/VR is used for remote training, virtual prototyping, and real-time quality control. Healthcare organizations use AR/VR for remote surgery assistance, patient monitoring, and immersive therapy. Retailers leverage AR/VR for virtual product demonstrations, interactive showrooms, and customer engagement. The global enterprise AR/VR market is projected to reach $78.4 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate of 22% through 2030.
IoT Integration in AR/VR
IoT integration is making AR/VR environments more interactive and responsive. IoT sensors feed real-time data into AR/VR systems, enabling dynamic overlays and context-aware experiences. In industrial training, IoT-enabled AR/VR overlays live data on equipment, guiding workers through maintenance or repair tasks. This reduces errors, improves safety, and shortens training times. In healthcare, IoT sensors provide patient data for remote surgery assistance and monitoring, allowing specialists to collaborate in real time from different locations.
Retailers are also adopting IoT-integrated AR/VR to enhance customer experiences. Virtual product demonstrations can display live inventory data, while interactive showrooms allow customers to explore products in detail before making a purchase. These applications not only improve customer engagement but also provide valuable data for inventory management and sales optimization.
The technical implementation of IoT in AR/VR requires robust connectivity, low-latency data processing, and secure integration. Edge computing is often used to process sensor data locally, ensuring real-time responsiveness. Open APIs and interoperability standards are essential for integrating devices from different manufacturers. As AR/VR adoption grows, organizations should prioritize scalable platforms and strong security practices to protect sensitive data.
Key points of Manufacturing and Quality Control Practices

Agritech: Precision, Automation, and Data-Driven Farming
Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture uses IoT devices to monitor soil moisture, weather, and crop health, enabling farmers to use resources more efficiently and increase yields. Soil sensors measure moisture, pH, and nutrient levels, while weather stations track temperature, humidity, and rainfall. Drones and robotics automate planting, spraying, and harvesting, reducing labor costs and improving consistency. AI-powered precision spraying systems can identify weeds and apply herbicides only where needed, reducing chemical use by up to 75% and supporting sustainable farming practices.
The benefits of precision agriculture are measurable. Smart irrigation systems, for example, use soil and weather data to water crops only when needed, resulting in water savings of up to 30% and yield increases of 15–25%. These systems help farmers adapt to changing climate conditions and reduce environmental impact. In addition, IoT-enabled pest monitoring allows for early detection and targeted intervention, minimizing crop losses and reducing the need for broad-spectrum pesticides.
Implementation of precision agriculture requires investment in sensors, connectivity infrastructure, and data analytics platforms. Farmers must select the right mix of technologies based on their specific crops, climate, and operational scale. Training and support are essential to ensure successful adoption and maximize return on investment.
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are transforming agricultural operations by reducing labor needs and improving efficiency. AI-driven robots can identify weeds, apply fertilizer, or harvest crops with high accuracy. Autonomous drones and ground robots are widely used for crop monitoring, mapping, and direct intervention. These technologies enable farmers to manage larger areas with fewer resources and respond quickly to emerging challenges.
A key case study is smart irrigation. Smart Irrigation IoT-based systems use real-time soil and weather data to optimize watering schedules. This approach not only conserves water but also ensures crops receive optimal hydration, leading to higher yields and better quality. In livestock farming, IoT-enabled wearable devices track the location, health, and activity of animals, allowing for early detection of illness and improved animal welfare.
The adoption of automation and robotics in agriculture is supported by government incentives, research partnerships, and industry collaborations. Farmers are encouraged to start with pilot projects, measure outcomes, and scale successful solutions. Integration with existing farm management systems and cloud platforms is critical for seamless operation and data-driven decision-making.

Data-Driven Decision Making
Big data and cloud computing are central to modern agriculture. Farmers use cloud-based platforms to analyze sensor data, predict pest outbreaks, and optimize planting schedules. Digital twin technology allows for real-time simulation and optimization of farm operations, enabling scenario planning and resource allocation. These tools help farmers make informed decisions, reduce waste, and improve profitability.
Data-driven agriculture also supports compliance with environmental regulations and sustainability goals. By tracking inputs and outputs, farmers can document their practices and demonstrate progress toward reducing carbon emissions and conserving resources. Integration with supply chain systems enables traceability from farm to table, meeting consumer demand for transparency and quality.
To succeed with data-driven agriculture, farmers need access to reliable data, user-friendly analytics tools, and ongoing support. Partnerships with technology providers, research institutions, and industry groups can help bridge knowledge gaps and accelerate adoption.
Key points of Agritech

CleanTech: Renewable Energy, Smart Grids, and Environmental Monitoring
Renewable Energy Technologies
CleanTech aims to reduce environmental impact through renewable energy and efficient resource use. IoT enables real-time monitoring and control of solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems. In 2025, solar PV is expected to account for half of all CleanTech capacity additions, with solid-state batteries and green hydrogen gaining traction. Perovskite solar cells offer higher efficiency and lower cost than traditional silicon cells, while green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy for industrial applications.
Technical innovations in CleanTech are driven by the need for reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. IoT sensors monitor performance, detect faults, and optimize energy production. Solid-state batteries provide improved energy density and safety for storage, supporting the integration of intermittent renewables into the grid. These technologies are essential for meeting global climate targets and supporting the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Implementation of renewable energy systems requires careful planning, site assessment, and integration with existing infrastructure. Utilities and independent power producers are investing in digital platforms, predictive maintenance, and remote monitoring to maximize uptime and efficiency. Collaboration with technology providers and regulatory agencies ensures compliance and access to incentives.
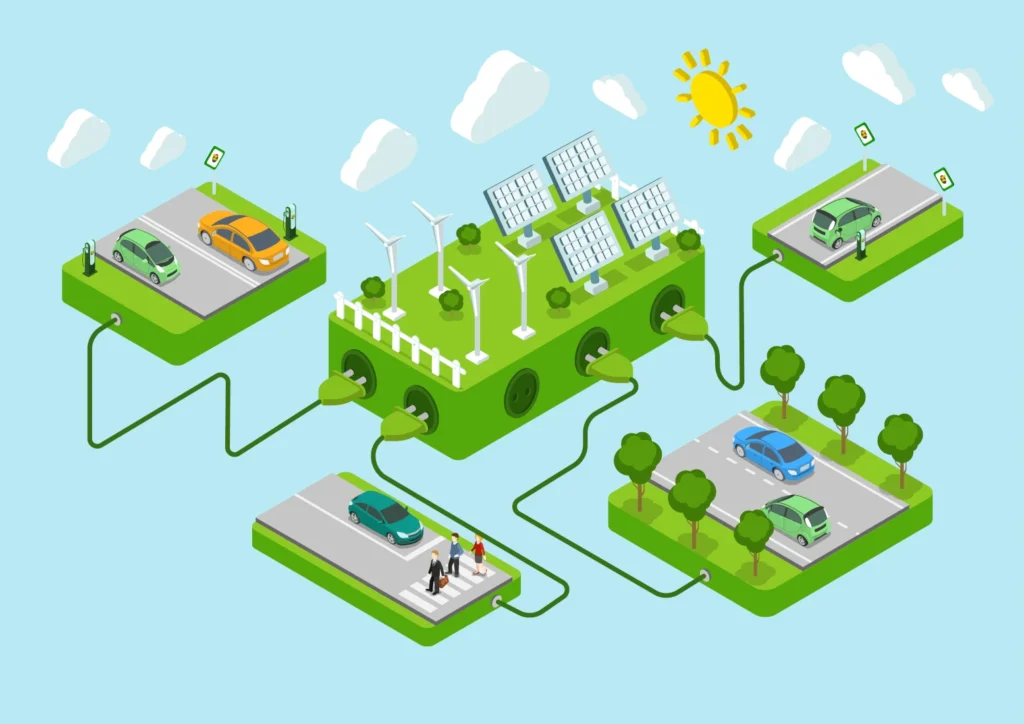
Smart Grids and Decentralized Energy
Smart grids use IoT sensors to balance supply and demand, integrate renewables, and reduce waste. Decentralized systems like microgrids allow communities to generate and manage their own power, increasing resilience and reducing reliance on centralized infrastructure. Utilities are investing in digital infrastructure, microgrids, and AI-driven management systems to enhance reliability and support distributed energy resources.
A notable case study is the implementation of IoT-enabled smart grids, which provide real-time data on energy use, helping utilities optimize distribution and reduce outages. These systems support demand response, peak shaving, and integration of electric vehicles, contributing to grid stability and cost savings. Microgrids are particularly valuable in remote or disaster-prone areas, where they can operate independently during grid outages.
The transition to smart grids and decentralized energy requires investment in sensors, communication networks, and control systems. Interoperability and cybersecurity are critical, as grids become more complex and interconnected. Utilities and regulators must work together to develop standards, ensure data privacy, and support innovation.
Environmental Monitoring
IoT devices play a vital role in environmental monitoring, tracking air and water quality, managing waste, and monitoring emissions. This data supports compliance with environmental regulations and helps companies reduce their carbon footprint. AI and digital platforms are optimizing supply chains, energy management, and predictive maintenance across CleanTech sectors.
Environmental monitoring systems use a variety of sensors to collect data on pollutants, greenhouse gases, and resource consumption. This information is used to identify trends, detect anomalies, and inform policy decisions. Companies can use environmental data to demonstrate sustainability, improve operational efficiency, and meet stakeholder expectations.
Implementation of environmental monitoring solutions requires collaboration with government agencies, research institutions, and technology providers. Data integration, visualization, and reporting tools are essential for turning raw data into actionable insights. Ongoing maintenance and calibration of sensors ensure data accuracy and reliability.
Key points of CleanTech

Technical Challenges and Solutions in IoT
Data Security and Privacy
IoT systems collect sensitive data, making security a top concern. Security attacks on IoT devices increased by 107% in the first half of 2024 compared to the same period in 2023. Encryption, secure protocols, and regular updates are essential. One in three data breaches now involves an IoT device, highlighting the need for robust security measures. International standards such as ISO/IEC 27404 and ETSI EN 303 645 set baseline requirements for device security, including password management, software updates, and data protection.
Organizations are encouraged to adopt a layered security approach, combining secure boot, hardware-backed keys, over-the-air (OTA) updates, network segmentation, and continuous monitoring. The IoT Security Maturity Model (SMM) and the Cloud Security Alliance’s IoT Security Controls Framework provide structured approaches for assessing and improving security posture. Regulatory initiatives in the EU, UK, and US are driving manufacturers to adopt secure-by-design principles and participate in certification and labelling programs.
Implementation of security best practices requires collaboration across the supply chain, from device manufacturers to end users. Regular risk assessments, vulnerability management, and employee training are essential for maintaining a strong security posture.
Interoperability
Interoperability is a major challenge in IoT deployments, as devices from different manufacturers must work together seamlessly. Open standards and APIs are essential for ensuring compatibility and supporting future growth. Protocols such as MQTT, CoAP, and Matter are widely adopted for device communication, while frameworks like LwM2M support device management and firmware updates.
Case studies show that open standards and modular platforms are key to supporting large-scale IoT deployments. Organizations should prioritize solutions that support industry standards and offer flexible integration options. Participation in industry alliances and standards bodies can help shape the development of new protocols and ensure alignment with best practices.
To address interoperability challenges, organizations should conduct thorough testing, maintain detailed documentation, and establish clear integration guidelines. Collaboration with technology partners and ongoing monitoring of industry trends are essential for staying ahead of emerging issues.
Scalability
As IoT networks grow, managing large numbers of devices becomes increasingly complex. The number of connected IoT devices reached 18.8 billion by the end of 2024, and by 2025, IoT devices are projected to generate 73.1 zettabytes of data. Edge computing and cloud management platforms support scalability by distributing processing and storage across the network. For a bit of understanding how much data that is: 73.1 ZB×1012 = 73,100,000,000,000 GB. Or in Terabytes: 73,100,000,000 TB. That is an unimaginable amount of data.
Scalable IoT architectures are modular and support dynamic resource allocation, allowing organizations to add or remove devices as needed. Automated device onboarding, remote management, and over-the-air updates are essential for maintaining large deployments. Data analytics platforms must be capable of handling high volumes of data and providing real-time insights.
Organizations should plan for scalability from the outset, selecting platforms and technologies that can grow with their needs. Regular performance testing, capacity planning, and investment in infrastructure are critical for supporting long-term growth.
Key points of Technical Challenges in IoT


Final Thoughts on IoT & Emerging Technologies
IoT is the backbone of many emerging technologies, enabling new applications in AR/VR, Agritech, and CleanTech. By connecting devices and systems, IoT supports real-time data collection, automation, and smarter decision-making. As these technologies continue to develop, professionals who understand their technical foundations and practical uses will be best positioned to lead in electronics, manufacturing, and digital transformation. For more technical resources and updates, visit www.designtodevice.com.
About DesignToDevice
DesignToDevice delivers electronics manufacturing solutions for startups and established businesses. From prototyping to full-scale production, we support your project at every stage. Our focus on quality, transparency, and design for manufacturing (DFM) ensures your ideas move smoothly from concept to finished product.
Why trust DesignToDevice?
At DesignToDevice, our content is written and reviewed by professionals with hands-on experience in electronics manufacturing and design. We reference recognized industry standards and certifications, and we regularly update our articles to reflect the latest developments. Our commitment is to provide clear, accurate, and practical information you can rely on.
Internal Links (DesignToDevice.com)
External Links (Sources)
Sign Up To Our Newsletter
We send newsletters when new blog posts go live. Timely insights crafted for industry professionals.